When you type a website address into your browser, a complex process happens behind the scenes to fetch the correct webpage. This process is called domain lookup. Understanding how it works can help troubleshoot website issues and improve loading speed.
In this guide, we’ll explain how domain lookup works, step by step, with simple illustrations and examples to enable you understand effectively.
What Is the Domain Lookup Process?
The domain lookup process is how your computer translates a human-friendly domain name (e.g., www.telahosting.com) into an IP address that computers can understand (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
This process relies on the Domain Name System (DNS), which acts like the internet’s phonebook, mapping domain names to IP addresses. In other words, since computers don’t understand words like telaHosting.com, they rely on DNS to translate human-friendly names into machine-readable IP addresses.
Illustration of the Domain Lookup Process
Imagine DNS as a directory service. If you want to call a friend but don’t remember their phone number, you look it up in your phonebook. Similarly, DNS translates domain names into the correct IP addresses.
Analogy: Looking for a Friend’s House in Lagos
Think of domain lookup like searching for a friend’s house in a big city like Lagos:
- You ask yourself: “Where does my friend live?” (Your computer checks its cache).
- You call a relative to ask: If you don’t remember, you ask someone else (Recursive DNS Resolver).
- They guide you to a street name: Your relative directs you to an area (Root DNS Server).
- You reach the street and ask security: Security tells you which compound (TLD Server).
- You find the house number: The security confirms the exact house number (Nameserver).
- You enter the house: You now have the correct location (Website loads).
This is exactly how domain lookup works!
For more details, visit Cloudflare’s Guide to DNS.
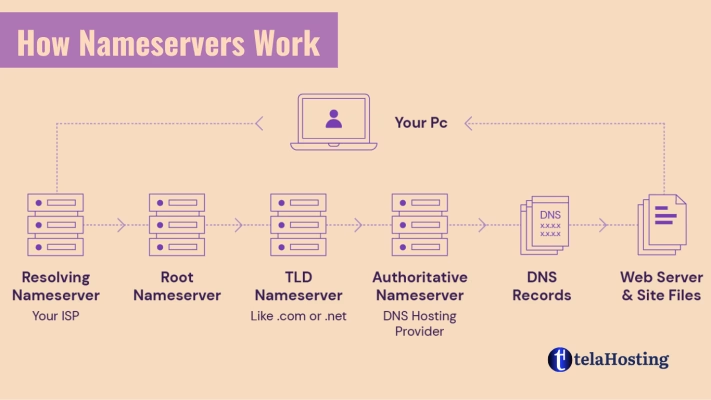
Step-by-Step Process of a Domain Lookup
- User Requests a Website: You type
www.telahosting.cominto your browser. Your device checks its local cache for a recent lookup. - Query Sent to a Recursive Resolver: If the domain is not in your cache, the request goes to a recursive resolver (usually provided by your ISP or a public DNS like Google DNS
8.8.8.8). - Checking the Root Nameservers: The recursive resolver contacts one of the root nameservers, which directs it to the correct Top-Level Domain (TLD) nameserver.
- Querying the TLD Nameserver: The TLD nameserver (e.g., for
.comdomains) responds with details of the authoritative nameserver. - Retrieving the IP Address: The authoritative nameserver provides the final IP address for the domain (e.g.,
192.168.1.1). - Website Loads on Your Browser: Your browser uses the IP address to retrieve and load the website. The IP address is stored in your device’s cache for faster access next time.
How to Check Your Domain Lookup Speed
If your website loads slowly, checking your domain lookup speed can help identify DNS-related issues.
Tools to Check DNS Lookup Speed:
- Nslookup:
nslookup www.example.com - Dig:
dig www.example.com - Traceroute:
tracert www.example.com - Online Tools: MXToolBox, Google Admin Toolbox
Common DNS Issues and How to Fix Them
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Slow DNS Resolution | ISP’s default DNS is slow | Use faster DNS like Google (8.8.8.8) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) |
| Website Not Loading | Incorrect DNS records | Check and update DNS records in your hosting account |
| DNS Propagation Delay | Recent DNS changes | Wait 24-48 hours for global updates |
| Error: Server Not Found | Incorrect nameservers | Verify nameserver settings in domain registrar panel |
FAQs
Q1: What happens if a domain lookup fails?
If the lookup fails, your browser will display an error like “Server Not Found.” You may need to check DNS settings or switch to a faster DNS provider.
Q2: How can I speed up my domain lookup process?
Using a fast and reliable DNS provider like Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) can improve lookup speed.
Q3: How long does DNS propagation take?
DNS changes typically take 24-48 hours to fully propagate worldwide.
Q4: How can I test if my DNS is working correctly?
Use tools like nslookup, dig, or online checkers like WhatsMyDNS to verify DNS records.
Conclusion
Understanding the domain lookup process helps you troubleshoot website issues and optimize your site’s loading speed. By using reliable DNS providers, monitoring lookup times, and ensuring accurate DNS settings, you can enhance website performance. Need fast and secure DNS services? Get expert hosting and domain solutions at telaHosting! 🚀