
Have you ever wondered how your browser finds the website you want to visit when you type in a domain name like www.telahosting.com? The answer lies in something called nameservers. Nameservers are a critical part of the internet, acting as a bridge between your domain name and the hosting service where your website’s data is stored.
What Are Nameservers?
A nameserver is like a directory that tells your computer where to find the server hosting a website. When you type a website’s domain name into your browser, the nameserver connects that name to the correct IP address of the server storing the website’s files.
For example:
- When you enter www.jumia.com.ng, the nameserver translates it into the server’s IP address, such as 192.168.10.15, so your browser can load the site.
In our last article, we discussed extensively what a domain name is and how it works in relation to IP addresses. You might want to take a look at that here as this will also assist you in understanding better while nameservers exist.
How Nameservers Work
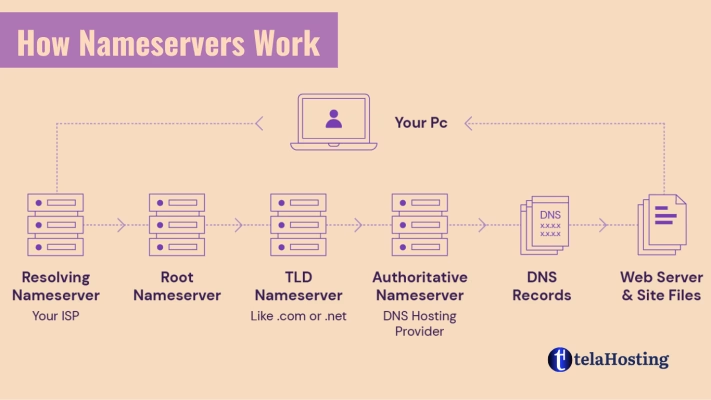
Let’s break it down step by step:
- You Type a Domain Name:
Imagine you’re visiting www.paystack.com. You type the domain name into your browser. - DNS Query Begins:
Your browser asks the DNS (Domain Name System) for the IP address of the domain. This query goes to the nameserver linked to the domain name. - Nameserver Responds:
The nameserver looks up the domain name in its records and finds the corresponding IP address (e.g., 102.123.45.67). - Connection Established:
Your browser connects to the hosting server at the IP address provided, and the website loads.
Nameservers as Middlemen
Think of nameservers as middlemen. If you ask someone for the address of a popular restaurant in Lagos, they consult their memory (or a directory) and give you the correct address. Nameservers do the same thing, they look up a domain name and return the right IP address.
Where Are Nameservers Used?
Nameservers are typically set when you register a domain name and link it to a hosting service. Common uses include:
- Setting Up a Website:
When you buy a domain from a registrar like telaHosting, you’ll need to point the domain to the hosting provider’s nameservers to make the website accessible online. - Email Hosting:
If your business uses custom email (e.g., [email protected]), nameservers are used to ensure email routing is correct. - Domain Transfers:
When transferring a domain between registrars, updating the nameservers is an essential step.
Relatable Examples
Scenario 1: Starting a Small Business Website
Imagine you just registered www.naijastyles.com.ng on telaHosting. To launch your website, you must set the nameservers provided by telaHosting, such as:
- ns1.telahosting.com
- ns2.telahosting.com
These nameservers tell the internet where your website’s files are stored so visitors can access them.
Scenario 2: Email Hosting for a School
A Nigerian school using [[email protected]] will set up nameservers to ensure emails are routed correctly through their hosting provider.
Common Nameserver Formats
Nameservers usually follow a standard format. Examples include:
- ns1.telahosting.com and ns2.telahosting.com (primary and secondary nameservers).
- Hosting-specific nameservers like da1.telahosting.com or da2.telahosting.com.
Relationship Between Nameservers, Domain Name, and Web Hosting
| Component | Definition | Role in Website Setup |
|---|---|---|
| Domain Name | A human-readable address for a website (e.g., www.telahosting.com). | Identifies the website on the internet. Linked to hosting through nameservers. |
| Nameservers | Servers that translate domain names into IP addresses (e.g., ns1.telahosting.com). | Acts as the directory that connects the domain name to the correct hosting server. |
| Web Hosting | A service that stores website files on a server, making them accessible online. | The provider where the website’s data and files are stored. Needs nameservers to point to it. |
How to Check and Update Nameservers
Updating nameservers is straightforward, especially with tools like those provided by telaHosting. Follow these steps:
- Log in to Your Domain Registrar:
Access the account where you registered your domain. - Locate the Nameserver Settings:
Look for the option to manage or update nameservers. - Enter New Nameservers:
Replace the old nameservers with the ones provided by your hosting provider (e.g., ns1.telahosting.com, ns2.telahosting.com). - Save Changes:
Once saved, allow up to 48 hours for the changes to propagate across the internet.
Why Nameservers Are Important
- Connect Domains to Hosting: Nameservers are the glue that links your domain name to the server hosting your website.
- Enable Website Access: Without nameservers, your domain won’t direct visitors to your website.
- Flexibility: Nameservers make it easy to switch hosting providers without changing your domain name.
- Email and Other Services: Nameservers also help route emails and manage other domain services.
FAQs
Q1: What happens if I don’t update my nameservers?
If you don’t update your nameservers after purchasing hosting, your domain won’t point to your website, and visitors won’t be able to access it.
Q2: How long do nameserver changes take?
Nameserver updates usually take a few minutes to a few hours, but DNS propagation can take up to 48 hours worldwide.
Q3: Can I use nameservers from one host with another hosting provider?
No, you must use the nameservers provided by your hosting provider. For example, if telaHosting is your host, you’ll use their nameservers.
Q4: How do I know which nameservers to use?
Your hosting provider (e.g., telaHosting) will provide the nameservers to use when you sign up for a hosting package.
Q5: Can nameservers affect my website’s speed?
Yes, slow or misconfigured nameservers can lead to delays in resolving your domain, affecting the time it takes for your website to load.
Conclusion
Nameservers play a vital role in connecting domain names to hosting services, ensuring that visitors can access your website seamlessly. Whether you’re setting up a small business website, managing email hosting, or transferring a domain, understanding how nameservers work is essential for anyone looking to establish an online presence.
Ready to take the next step? Visit telaHosting today to register your domain and get reliable hosting services.